
1. Symptoms
o Common symptoms of candida are gas, headaches or migraines, exhaustion, cravings for food or alcohol, anxiety, inability to think, hyperactivity, diarrhea, hyperactivity, constipation, itching, acne, depression, inflammation of the sinus passages, difficulty with memory, coughing and earaches, problems with libido, indigestion and reflux, and chronic pain. The symptoms can vary between different systems in the body.
Stool Sample
o Testing for candida usually begins with a stool analysis, which examines the levels of bacteria and microflora, yeast and pathogens. A stool sample will help determine if yeast is the source of symptoms.
Blood Test
o Candida can also be tested through a blood sample from a tube or finger prick, which is sent to a lab to determine what antibodies are present. The blood sample can be taken at a doctor's office, lab or at home.
Throat Culture
o A throat culture might be taken to test for candida or diagnose the growth of other bacteria or fungi in the throat. During the test, a doctor swabs the back of the throat. The sample is put in a cup that allows it to grow. If the infection grows, the culture will be positive and a lab technician will use chemical tests and a microscope to determine what type of infection is causing the symptoms.
Tissue Biopsy
o If the infection is systemic, a doctor may take samples from various organs and a pathologist will review the tissue under a microscope. This will help to determine the extent to which candida has spread.
Treatment
o The majority of candida infections may be treated with prescription medication or over-the-counter antifungals, but it often depends on the location of the infection. Most medications can be taken orally or as a topical cream. A serious or systemic candida infection may require hospitalization.
Complications
o If candida is left untreated, it can rupture the intestinal lining and enter the bloodstream, which can lead to the development of lethal diseases. As it spreads to other parts of the body, it multiplies and can cause problems in the joints, muscle pain, fatigue, urinary tract infections and problems with other organs. If the body's immune system is not capable of fighting off the infection, it can result in blood poisoning (septicemia). In this case, the infection has spread throughout the body's tissues and lymphatic system.
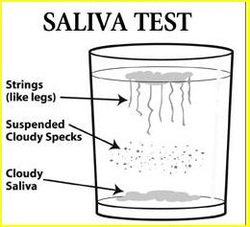
Click on "Saliva Test" for more detailed information...


